2023-07 Monthly Archive
What does bring up a CPU mean?
restore_processor_state() Kernel
Intel SGX DCAP
Data Center Attestation Primitives
Intel SGX PCCS
Provisioning Certificate Caching Service.
Design Guide for Intel® SGX Provisioning Certificate Caching Service
struct kvm_apic_map KVM
struct kvm_apic_map {
struct rcu_head rcu;
u8 mode;
u32 max_apic_id;
union {
struct kvm_lapic *xapic_flat_map[8];
struct kvm_lapic *xapic_cluster_map[16][4];
};
// From each
struct kvm_lapic *phys_map[];
};
struct flush_tlb_info Kernel
//...
struct flush_tlb_info {
/*
* We support several kinds of flushes.
*
* - Fully flush a single mm. .mm will be set, .end will be
* TLB_FLUSH_ALL, and .new_tlb_gen will be the tlb_gen to
* which the IPI sender is trying to catch us up.
*
* - Partially flush a single mm. .mm will be set, .start and
* .end will indicate the range, and .new_tlb_gen will be set
* such that the changes between generation .new_tlb_gen-1 and
* .new_tlb_gen are entirely contained in the indicated range.
*
* - Fully flush all mms whose tlb_gens have been updated. .mm
* will be NULL, .end will be TLB_FLUSH_ALL, and .new_tlb_gen
* will be zero.
*/
// mm 表示要 flush 的 mm,可以为空
struct mm_struct *mm;
// start 和 end 表示要 flush 的 range
unsigned long start;
unsigned long end;
// 是哪一个 CPU 发起的
unsigned int initiating_cpu;
// 这是一个 bool 类型的(bool 就是 u8)
// whether page tables are about to be freed after this TLB flush.
// 表示是否在这次 flush 之后,对应的页表要被移除。
// 比如函数 flush_tlb_mm() 会把这个设置为 true,因为
u8 freed_tables;
// ...
};
native_flush_tlb_multi() Kernel
这个函数就是默认用来做 TLB Flush 的,当不是一个虚拟机时,Kernel 会调用这个直接来 flush,当是时,会尝试其他使用了 PV 的 method,如果都不行才会用这个方法,这个方法是 unaware PV 的。
STATIC_NOPV void native_flush_tlb_multi(const struct cpumask *cpumask,
const struct flush_tlb_info *info)
{
// 做一下记录,但是有可能在记录了之后,最后却没有做 TLB flush 的情况。
count_vm_tlb_event(NR_TLB_REMOTE_FLUSH);
if (info->end == TLB_FLUSH_ALL)
// Flush all entries in the TLB
trace_tlb_flush(TLB_REMOTE_SEND_IPI, TLB_FLUSH_ALL);
else
// Flush range of entries in the TLB
trace_tlb_flush(TLB_REMOTE_SEND_IPI, (info->end - info->start) >> PAGE_SHIFT);
if (info->freed_tables) {
// if page tables are getting freed, we need to send the
// IPI everywhere, to prevent CPUs in lazy TLB mode from tripping
// up on the new contents of what used to be page tables, while
// doing a speculative memory access.
// 如果页表正在被移除,我们需要对所有的 CPU 发送 IPI,即使正在 lazy TLB mode
// 的 CPU,因为如果页表被移除了,而 TLB 还没刷,那么曾经页表那个地方的新的内容
// 会因为 speculative memory access 而被 get 到。
on_each_cpu_mask(cpumask, flush_tlb_func, (void *)info, true);
} else {
// If no page tables were freed, we can skip sending IPIs to
// CPUs in lazy TLB mode. They will flush the CPU themselves
// at the next context switch.
on_each_cpu_cond_mask(tlb_is_not_lazy, flush_tlb_func, (void *)info, 1, cpumask);
}
}
tlb_is_not_lazy() Kernel / Lazy TLB mode
When some CPU starts running a kernel thread, the kernel sets it into lazy TLB mode. When requests are issued to clear some TLB entries, each CPU in lazy TLB mode does not flush the corresponding entries; however, the CPU remembers that its current process is running on a set of Page Tables whose TLB entries for the User Mode addresses are invalid. As soon as the CPU in lazy TLB mode switches to a regular process with a different set of Page Tables, the hardware automatically flushes the TLB entries, and the kernel sets the CPU back in nonlazy TLB mode.
static bool tlb_is_not_lazy(int cpu, void *data)
{
return !per_cpu(cpu_tlbstate_shared.is_lazy, cpu);
}
Guest Partition
Hyper-V supports isolation in terms of a partition. A partition is a logical unit of isolation, supported by the hypervisor, in which operating systems execute.
Partition 之间是存在父子关系的。
The Microsoft hypervisor must have at least one parent, or root, partition, running Windows. The virtualization management stack runs in the parent partition and has direct access to hardware devices. The root partition then creates the child partitions which runs the guest operating systems. A root partition creates child partitions using the hypercall API.
Each partition has a set of privileges assigned by the hypervisor. Privileges control access to synthetic MSRs or hypercalls.
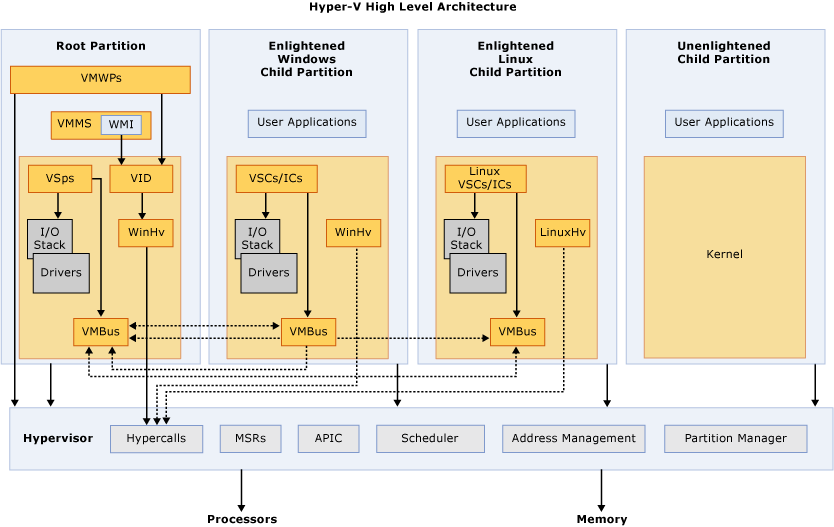
| [Partition | Microsoft Learn](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/virtualization/hyper-v-on-windows/tlfs/partition-properties) |
| [Hyper-v Architecture | Microsoft Learn](https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/virtualization/hyper-v-on-windows/reference/hyper-v-architecture) |
Microsoft VSM (Virtual Secure Mode)
Virtual Secure Mode | Microsoft Learn
page_address() Kernel
输入是一个 struct page,返回这个 struct page 所描述的 page 的虚拟地址。
#define page_address(page) lowmem_page_address(page)
PAGE_OFFSET Kernel
虽然内核空间占据了每个虚拟空间中的最高 1GB 字节,但映射到物理内存却总是从最低地址(0x00000000)开始。对内核空间来说,其地址映射是很简单的线性映射。0xC0000000 就是物理地址与线性地址之间的位移量,在 Linux 代码中就叫做 PAGE_OFFSET.
PAGE_OFFSET 只对内核空间有效。
__va() Kernel
传进来的是一个 PA(物理地址),为什么加了 PAGE_OFFSET 就变成 VA 了?可以看一下 PAGE_OFFSET 的作用^。
传进来的 PA 只能是内核空间的 PA,不能是用户空间的 PA,否则计算将错误。
#define __va(x) ((void *)((unsigned long)(x)+PAGE_OFFSET))
page_to_virt() Kernel
传进来的是一个 struct page,返回的是其所描述的页的 VA。
virt_to_page() Kernel
传进来的是一个页的 VA,返回的是这个页对应的 struct page。
#define virt_to_page(kaddr) pfn_to_page(__pa(kaddr) >> PAGE_SHIFT)
kvm_physical_memory_addr_from_host() QEMU
找到传进来的 ram (HVA) 属于哪一个 KVMSlot,计算出相对于 KVMSlot base HVA 的 offset,将其加上这个 KVMSlot 的基本 GPA,并据此将其转换为 GPA,放在 phys_addr 中返回。
int kvm_physical_memory_addr_from_host(KVMState *s, void *ram, hwaddr *phys_addr)
{
KVMMemoryListener *kml = &s->memory_listener;
int i, ret = 0;
kvm_slots_lock();
for (i = 0; i < s->nr_slots; i++) {
KVMSlot *mem = &kml->slots[i];
if (ram >= mem->ram && ram < mem->ram + mem->memory_size) {
*phys_addr = mem->start_addr + (ram - mem->ram);
ret = 1;
break;
}
}
kvm_slots_unlock();
return ret;
}
struct CPUState QEMU
struct CPUState {
//...
// 好像是 vCPU synchronize 用的?
// 在每次 QEMU 去发 ioctl 让 VCPU RUN 之前,QEMU 会 check
// vcpu_dirty 是否为 true,如果是,那么设置为 false,并
// kvm_arch_put_registers(cpu, KVM_PUT_RUNTIME_STATE);
// 这个会写入很多个 registers,来让其重新 clean。
bool vcpu_dirty;
//...
// See dirty ring mode^
// Points to the KVM dirty ring for this CPU when KVM dirty ring is enabled.
// 是 KVM 和 QEMU 共享的内存
// cpu->kvm_dirty_gfns = mmap(NULL, s->kvm_dirty_ring_bytes...
struct kvm_dirty_gfn *kvm_dirty_gfns;
}
iov_discard_front() / iov_discard_front_undoable() QEMU
iov_discard_front 直接传了 NULL 进去,说明是不 undoable 的。
iov_discard_front
iov_discard_front_undoable(iov, iov_cnt, bytes, NULL);
从 iov 的第一个 buffer 开始,一直 discard,直到 discard 够 bytes size。如果 discard 到了第 i 个 buffer,有富余,那么只 discard 应该 discard 的部分。
size_t iov_discard_front_undoable(struct iovec **iov,
unsigned int *iov_cnt,
size_t bytes,
IOVDiscardUndo *undo)
{
size_t total = 0;
struct iovec *cur;
//...
for (cur = *iov; *iov_cnt > 0; cur++) {
if (cur->iov_len > bytes) {
//...
cur->iov_base += bytes;
cur->iov_len -= bytes;
total += bytes;
break;
}
bytes -= cur->iov_len;
total += cur->iov_len;
*iov_cnt -= 1;
}
*iov = cur;
return total;
}
host-phys-bits QEMU
这个透传的是 0x80000008,也就是 MAXPHYADDR,一般是 52。并不是
cat /proc/cpuinfo | grep '^address sizes'
所输出的内容。也就是 CPU 实际支持的物理地址宽度。这个宽度对应 cpuinfo_x86 里的 x86_phys_bits。
x86_phys_bits 在刚开始会被初始化为 52,但是后面会根据其它因素减小,比如 TME 的 keyID 就会影响这个大小,如果有 63 个 keyID,那么 x86_phys_bits 就要少 6 位,毕竟也是占物理内存地址空间的。
XBZRLE
Xor Based Zero Run Length Encoding
XBZRLE 是一个 QEMU migration 的优化特性。
源端 cache 已经发送的内存页,下次发送该页时对比,只发送变化部分的数据。
CPLD
Complex Programmable Logic Device.
NFS setup for remote live migration
src:
dnf install nfs-utils
systemctl start nfs-server.service
systemctl enable nfs-server.service
systemctl status nfs-server.service
mkdir -p /tdx/share
# export to all ip
echo "/tdx/share/ *(rw,sync,no_root_squash)" >> /etc/exports
exportfs -rva
systemctl stop firewalld
dst:
sudo yum install nfs-utils
mkdir -p /tdx/share
sudo mount -t nfs 192.168.99.79:/tdx/share /tdx/share
在 Yum 中安装指定版本的软件 (CentOS)
yum list | grep <name>
yum install <output>
strcut kvm_apic_map
struct kvm_apic_map {
struct rcu_head rcu;
u8 mode;
u32 max_apic_id;
union {
struct kvm_lapic *xapic_flat_map[8];
struct kvm_lapic *xapic_cluster_map[16][4];
};
// map from apic id to *struct kvm_lapic*
struct kvm_lapic *phys_map[];
};
Preemption timer
Preemption Timer 是一种可以周期性使 VCPU 触发 VMExit 的一种机制。即设置了 Preemption Timer 之后,可以使 VCPU 在指定的 TSC cycle (注意文章最后的 rate) 之后产生一次 VMExit。
Preemption timer 是受硬件支持的,而不是纯软件的 timer。
Introduction to VT-x Preemption Timer - L
put_page() / get_page() / free_page() KVM
get_page 与 put_page 是对应的。
get_page 获得 page 的使用,page 的 page_count 计数加一,相应的,put_page 释放 page 的使用,page 的 page_count 计数减一。
简单来说,put_page() 就是释放一个 page。
那么 put_page() 和 free_page() 的区别是什么?
作用是一样的,但是看起来有一些细微的差别:
Memory Management APIs — The Linux Kernel documentation 在这里找 __free_pages()。
struct vm_fault Kernel
struct vm_fault {
const struct {
struct vm_area_struct *vma; /* Target VMA */
// 这个 page fault 发生在这个 VMA 里的第几个 page?
// 看这个函数 linear_page_index()
pgoff_t pgoff;
unsigned long address; /* Faulting virtual address - masked */
unsigned long real_address; /* Faulting virtual address - unmasked */
};
//...
};
kvm_tdp_mmu_zap_sp KVM
x86_emulate_ops / emulate_ops
static const struct x86_emulate_ops emulate_ops = {
.vm_bugged = emulator_vm_bugged,
.read_gpr = emulator_read_gpr,
.write_gpr = emulator_write_gpr,
//...
.set_xcr = emulator_set_xcr,
};
x86_emulate_ops 函数看看就好,实际上也很少有人放弃 vmx 直接软件模拟,都是一些用来模拟的 helper。
KVM page track
In file arch/x86/include/asm/kvm_page_track.h.
struct kvm_page_track_notifier_node KVM
一些关于 page trace 的函数钩子,用来在特定的时刻触发。
struct kvm_page_track_notifier_node {
struct hlist_node node;
// It is called when guest is writing the write-tracked page
// and write emulation is finished at that time.
void (*track_write)(struct kvm_vcpu *vcpu, gpa_t gpa, const u8 *new,
int bytes, struct kvm_page_track_notifier_node *node);
// It is called when memory slot is being moved or removed
// users can drop write-protection for the pages in that memory slot
void (*track_flush_slot)(struct kvm *kvm, struct kvm_memory_slot *slot,
struct kvm_page_track_notifier_node *node);
};
// call trace for track_write()
emulator_write_phys / emulator_cmpxchg_emulated
kvm_page_track_write
n->track_write()
// call trace for track_flush_slot()
kvm_invalidate_memslot
kvm_arch_flush_shadow_memslot
kvm_page_track_flush_slot
n->track_flush_slot();
Semaphore in QEMU
QEMU 里 Semaphore 的底层实现使用了 Mutex。
qemu_sem_init() / qemu_sem_destroy() QEMU
因为 Mutex 里也有 init 和 destroy 的 API,所以 Semaphore 里也有这样的 API。
qemu_sem_post() QEMU
+1,可以理解为生产者。
qemu_sem_wait() QEMU
当不是 0 时 -1,当是 0 时,等待直到变成不是 0。可以理解为消费者。
qemu_sem_timedwait() QEMU
看起来是给 wait 加了一个时间上的限制。
Linux 睡眠状态
取决于所运行平台的能力和配置选项,Linux 内核能支持四种系统睡眠状态,睡眠深度从浅到深:
s2idle
Suspend-to-idle ("s2idle") is a system state in which all user space has been frozen, all I/O devices have been suspended and the only activity happens here and in interrupts (if any). In that case bypass the cpuidle governor and go straight for the deepest idle state available. Possibly also suspend the local tick and the entire timekeeping to prevent timer interrupts from kicking us out of idle until a proper wakeup interrupt happens.
Standby
Suspend-to-RAM
Hibernation
struct kvm_lapic KVM
LAPIC dedicated to my guest.
struct kvm_lapic {
// which vcpu this LAPIC belong to?
struct kvm_vcpu *vcpu;
// ...
bool apicv_active;
};
kvm_lapic->apicv_active KVM
字如其名。